The New Era of Connectivity: How Blockchain is Reshaping the Digital Landscape
Introduction of Blockchain Technology
Explore how blockchain technology is driving the digital revolution. Discover its rise and impact on various industries in this insightful article.
Overview of blockchain technology
Blockchain, essentially a digital ledger system, is ushering in a new era of the internet by allowing digital information to be distributed but not copied. This technology supports the backbone of a new type of internet in which digital information can be shared without the need for a central administrator.
Brief history and evolution of blockchain
Originating with the cryptocurrency Bitcoin in 2009, blockchain technology was created to support a transparent, verifiable, secure, and decentralized record of transactions. Its capacity to foster trust through its highly secure nature has led to its adoption beyond digital currencies and into various sectors of the digital world.
Importance of blockchain in today’s digital world
Blockchain is no longer just about cryptocurrencies. It’s transforming how we conduct business, interact, and secure data online. By promoting transparency, efficiency, and security, blockchain is steadily becoming a foundational technology in the digital age.
Transforming Financial Services of Blockchain Technology

Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Reducing reliance on traditional banking: DeFi uses blockchain to eliminate intermediaries in financial transactions. Decentralization not only speeds up processes but also reduces costs, making financial services more accessible.
- Examples of DeFi platforms and their impact: Platforms like Uniswap and MakerDAO allow users to lend, borrow, and trade without traditional financial institutions, fundamentally reshaping access to financial services.
- Future opportunities in DeFi: As DeFi grows, it could potentially replace many aspects of traditional banking, democratizing financial opportunities globally.
Improving Transaction Efficiency
- Faster transaction times compared to traditional banks: Blockchain can process transactions in mere minutes, even across borders, which traditional banking systems could take days to handle.
- Reduction in transaction fees: Without the need for intermediaries, transaction fees are considerably lower.
- Cross-border transactions made simple: Blockchain simplifies complex, multi-party cross-border transactions by providing a single, immutable record.
Enhancing Security and Transparency
- How blockchain increases trust through transparency: Each transaction is recorded transparently and cannot be changed, which builds trust among users.
- The role of encryption and secure transactions: Advanced cryptographic techniques ensure that all transactions are secure and protected from fraud.
- Case studies: Successful implementation in financial sectors: J.P. Morgan’s creation of the JPM Coin and Ripple’s payment systems underscore how major financial institutions are successfully using blockchain.
Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management of Blockchain Technology
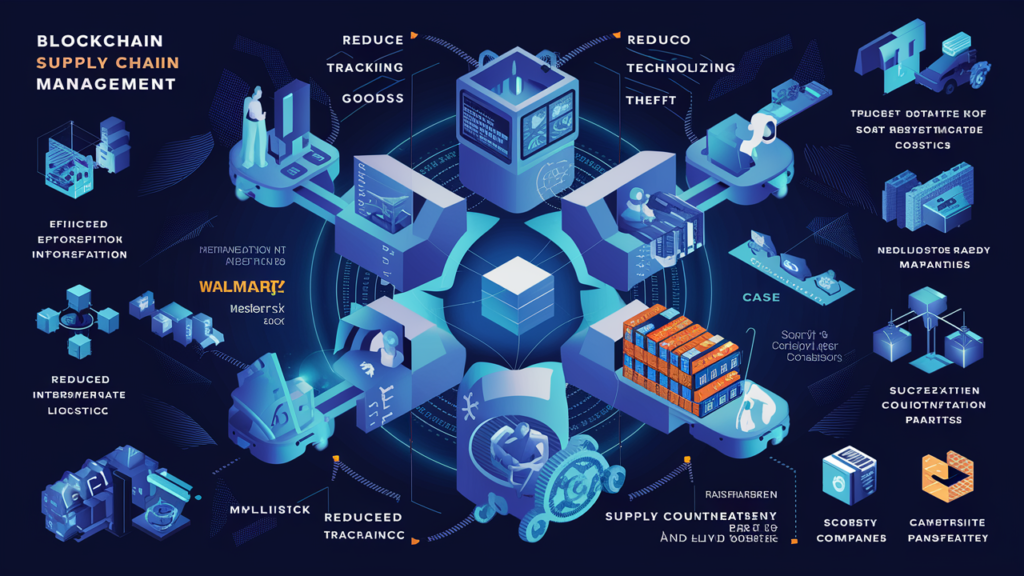
Tracking and Transparency
- Real-time tracking of goods: Blockchain provides updates in real-time on the whereabouts of goods, reducing loss.
- Reducing counterfeiting and theft: The clarity of blockchain’s record-keeping helps prevent fraud and theft in the supply chain.
- Improved transparency from origin to end consumer: Consumers can easily track the origin of the goods they purchase, increasing trust and satisfaction.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
- Streamlining logistics and operations: Integration of blockchain reduces delays and eliminates redundancies by providing one true ledger to all parties.
- Reducing intermediaries in the supply chain means fewer middlemen, resulting in fewer markups and more streamlined operations.
- Case examples of cost savings in global supply chains: Companies like Walmart and Maersk have implemented blockchain to manage their supply chains more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Increased Collaboration and Automation
- Facilitating smoother partnerships and alliances: Blockchain creates a shared platform that enhances collaboration across the supply chain.
- How smart contracts automate processes and payments: These self-executing contracts with the terms of agreement directly written into lines of code help in automating processes.
- Future trends in supply chain automation: Blockchain is paving the way for fully automated, transparent supply chains that are more resilient against disruptions.
Advancing Healthcare Systems

Secure Patient Data Management
- Enhancing privacy with blockchain-based records: Blockchain ensures that patient records are secure and accessible only to authorized individuals.
- Solutions to data breaches and medical fraud: The immutable nature of blockchain helps prevent unauthorized access and alterations to sensitive health information.
- Interoperability between different healthcare providers: Blockchain facilitates the secure sharing of patient data across various providers, enhancing continuity of care.
Drug Traceability
- Blockchain in combating counterfeit drugs: It ensures that drug shipments can be tracked from production to delivery, ensuring authenticity.
- Ensuring compliance with regulations: Blockchain helps healthcare providers adhere to regulations through secure, verifiable record-keeping.
- Impact on pharmaceutical supply chains: Enhanced traceability and transparency help in streamlining pharmaceutical supply chains, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency.
Improving Health Research
- Accelerating clinical trials: Blockchain can securely manage and track consent and results from multiple sites in clinical trials, leading to faster outcomes.
- Secure sharing of research data: Research institutions can share valuable data securely and transparently, speeding up research processes.
- Blockchain’s role in future health technologies: It holds signs of future applications where personal health data could be completely managed by individuals and shared securely for medical purposes.
Boosting Digital Identity and Security

Secure Identity Verification
- Simplifying identity checks while enhancing security: Blockchain provides a robust solution to secure and streamline identity verification processes.
- Use cases in government and private sectors: Governments and businesses are using blockchain to protect data and prevent identity theft.
- Impact on reducing identity theft: By providing a secure platform for storing personal data, blockchain significantly reduces the risk of identity theft.
Ownership and Control over Personal Data
- Empowering users to control their personal information: Blockchain puts control of personal data back in the hands of individuals, making data transactions transparent.
- Potential of blockchain in data privacy laws like GDPR: Blockchain can help organizations comply with privacy laws by providing improved data management tools.
- Future prospects in data ownership: The growing emphasis on data privacy could see blockchain become essential in managing and protecting personal data rights.
Facilitating Trusted Digital Interactions
- Blockchain in elections and public polls: It can secure the electoral process, reducing the likelihood of fraud and enhancing voter trust.
- Use in legal document verification: Blockchain ensures that legal documents are authentic and tamper-proof.
- Ensuring authenticity in academic certificates: Institutions can utilize blockchain to issue verifiable and unforgeable academic credentials.
The Future and Challenges of Blockchain

Potential Future Applications
- Exploring sectors ripe for blockchain disruption: Beyond finance and supply chains, sectors like real estate, energy, and entertainment are also poised for transformation.
- Emerging trends in blockchain technology: Areas like blockchain as a service (BaaS) and increasingly sophisticated smart contracts are on the rise.
- Predictions for blockchain’s global impact: The technology is set to redefine business practices, governance, and personal transactions on a global scale.
Current Limitations and Challenges
- Scalability issues and current technological limits: Blockchain networks, like those of Bitcoin, face challenges in scaling up to meet increasing demand without compromising performance or security.
- Legal and regulatory challenges: The decentralized nature of blockchain presents a significant challenge to existing legal frameworks, which can hinder its adoption.
- Environmental concerns related to blockchain technology: The energy consumption associated with blockchain, particularly proof of work (PoW) systems, is a growing environmental concern.
Educational and Development Needs
- The need for skilled blockchain professionals: The industry requires a massive influx of skilled professionals to innovate and maintain growing blockchain ecosystems.
- Importance of public and enterprise education: For blockchain to achieve widespread adoption, comprehensive education and training are crucial.
- The role of governments and institutions in fostering blockchain growth: Supportive policies and frameworks from governments and educational bodies will play a critical role in nurturing blockchain technology’s growth.
Conclusion
Reflecting on our detailed exploration, blockchain technology promises to revolutionize various facets of our digital and physical worlds. From transforming financial systems to improving healthcare privacy and beyond, its potential is vast yet not fully realized. As we navigate its advantages and confront its challenges, blockchain remains a pivotal development in our increasingly digital lives, setting the stage for a more secure, transparent, and efficient future.
Forbes: Blockchain Technology – What is it and How Does it Work?
Harvard Business Review: How Blockchain Will Change Organizations
TechCrunch: The Blockchain Technology
Wired: The Rise of Blockchain Technology
CNBC: Understanding Blockchain and Its Potential Impact
FAQs
- What is blockchain and how does it work?
Blockchain is a distributed database or ledger that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. As a database, blockchain stores information electronically in digital format. Its uniqueness lies in its security and decentralization: no single entity controls the data, and once entered, the data is irreversible and unchangeable. - How does blockchain influence the financial sector?
Blockchain technology has introduced concepts like cryptocurrencies and DeFi, reshaping the financial landscape by diminishing the role of traditional banks, cutting transaction costs, and speeding up processes, thereby making financial operations more accessible and efficient. - Can blockchain technology really improve healthcare privacy and data sharing?
Yes, by decentralizing the storage of medical records and securing them with encryption, blockchain significantly enhances privacy and security in healthcare. Furthermore, its characteristic transparency and immutability also facilitate better data sharing across providers. - What are the environmental impacts of blockchain?
The major environmental concern related to blockchain is its energy consumption, particularly the proof-of-work systems used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. However, alternative consensus mechanisms like proof-of-stake are being developed and adopted to mitigate these impacts. - What are some common misconceptions about blockchain?
A common misconception about blockchain is that it is only for cryptocurrencies. While it started with Bitcoin, blockchain’s potential extends much further, including secure digital transactions, supply chain management, and safeguarding personal data across various sectors.